
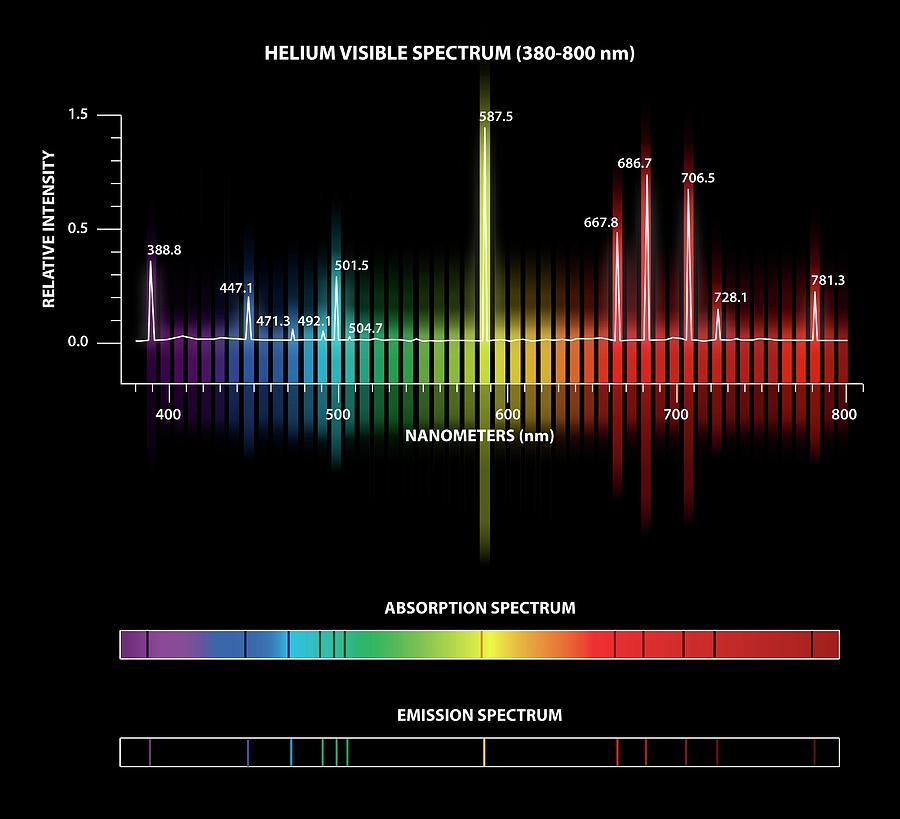
For highly ionized atoms, the lines are found in the extreme UV or x-ray region.Īs the relative intensity of the lines in an atomic spectrum varies with temperature, analysis of the lines in the spectrum of a star (say) can give an estimate of the temperature of the star’s surface (photosphere). Addeddate 00:19:10 Identifier in.ernet.dli.2015.212979 Identifier-ark ark:/13960/t14n4hx4m Ocr ABBYY FineReader 11. The graphic below shows the visible spectra for hydrogen. The light electronic transitions in atoms produces may not be in the visual part of the electromagnetic spectrum, but for atoms that are neutral or have lost only one or two electrons (yes, ‘atomic spectra’ refers to the line spectrum of ions too!), most lines are in the UV, visual, or near infrared. Of course, for an extragalactic object – a quasar, perhaps – you need more than one line to make a certain identification … because the universe is expanding (and so you don’t know how much just one line may have been redshifted). TYPES OF SPECTRA & HYDROGEN ATOMIC SPECTRUM 1) The emission spectrum is obtained due to emission of radiation from the substances. As the atomic electron energy levels are unique to each element, the lines in a spectrum (emission or absorption) can be used to identify the elements present in the source (a star, say) or gas between the source and us (e.g. The atomic spectra of hydrogen, helium, and mercury are scanned by hand using a grating spectrophotometer, which measures relative light intensity as a function. Atoms and the electromagnetic spectrum were linked: atoms emitted and absorbed light, and could be distinguished by their spectra (the pattern of emitted. Definition of an atomic Spectra is the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation produced or absorbed by an electron during transitions between different.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
